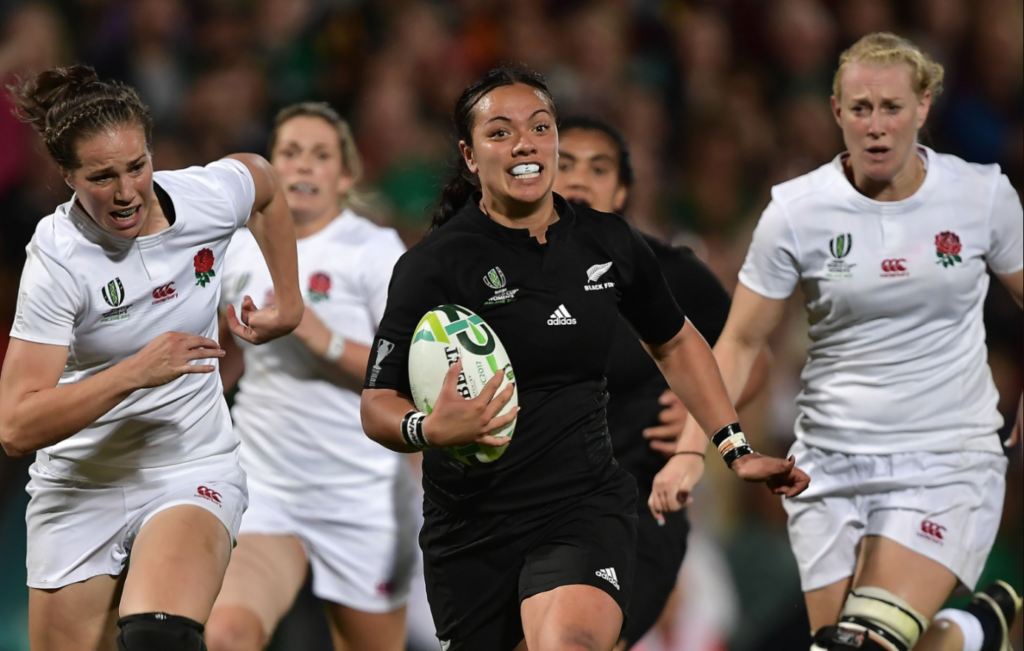
Rugby is a dynamic and exhilarating sport that has captured the hearts of millions around the world. Known for its physicality, strategic depth, and rich traditions, rugby is a game that brings together teams in a contest of strength, speed, and skill. But what exactly is rugby, and how did it become the global phenomenon it is today?
What is Rugby?
At its core, rugby is a team sport where players try to carry or kick a ball over the opponent’s goal line to score points. The game is played on a rectangular field, with each team trying to outmaneuver the other to gain possession and score. The unique aspect of rugby is its emphasis on teamwork, physical endurance, and strategic thinking. Players must be adept at both offensive and defensive roles, making rugby a truly all-around sport.
Brief History of Rugby
Rugby’s origins are famously traced back to 1823 at Rugby School in England when a young student named William Webb Ellis supposedly picked up a soccer ball and ran with it. While this tale is more legend than fact, it reflects the sport’s deep roots in English tradition. Over time, rugby evolved, split into different forms, and spread across the globe, influencing cultures and sporting communities worldwide.
The Different Types of Rugby
This is not just one game but a family of related sports, each with its own rules, style of play, and fan base.
Rugby Union
Rugby is the most widely recognized form of rugby. It is played with 15 players on each team and involves a mix of running, kicking, and tactical play. The game is known for its scrums, lineouts, and mauls, which add to its complexity and appeal.
Rugby League
Rugby League, a variant of rugby that emerged in 1895, is faster-paced and slightly more straightforward than Rugby Union. It features 13 players per side and a different set of rules, particularly concerning tackles and play restarts, making it a favorite in places like Australia and Northern England.
Rugby Sevens
Rugby Sevens is a shorter, more intense version of Rugby Union, played with seven players per team and over two halves of seven minutes each. The game’s rapid pace and high-scoring nature make it particularly exciting to watch and ideal for tournaments, including its inclusion in the Olympics.
Touch Rugby and Tag Rugby
For those looking for a less physical version of the sport, Touch Rugby and Tag Rugby offer non-contact alternatives. These variations emphasize speed, agility, and teamwork without the risk of heavy tackles, making them accessible to a broader audience, including children and beginners.
Rugby: The Most Popular Form
Basic Rules of Rugby
Rugby Union is governed by a complex set of rules designed to balance the physical and strategic elements of the game. Key aspects include the offside rule, the requirement to pass the ball backward, and the various ways to restart play, such as scrums and lineouts. The game is divided into two 40-minute halves, with the team scoring the most points winning the match.
Positions in Rugby Union
Rugby Union positions are divided into forwards and backs, each with specific roles. Forwards are typically larger and stronger, focusing on winning possession through scrums and lineouts, while backs are usually faster and more agile, responsible for exploiting gaps in the opposition’s defense.
Key Competitions and Tournaments in Rugby Union
The Rugby Union calendar is packed with prestigious tournaments. The Rugby World Cup is the pinnacle of the sport, held every four years, and brings together the best teams from around the globe. Other major competitions include the Six Nations Championship in Europe and The Rugby Championship in the Southern Hemisphere, both of which feature fierce rivalries and showcase top-level rugby.
Rugby League: A Fast-Paced Variant
Differences Between Rugby Union and Rugby League
While Rugby and Rugby League share a common ancestry, they differ significantly in gameplay. Rugby League has fewer players, simpler rules regarding possession after tackles, and a greater emphasis on continuous play, making it faster and often higher scoring than Union.
Basic Rules of Rugby League
Rugby League is played with 13 players on each team, and the game is divided into two 40-minute halves. Unlike Rugby Union, where a tackled player can be contested for the ball, in Rugby League, the tackled player must play the ball backward, leading to a more fluid and fast-paced game.
Popular Rugby League Tournaments
Rugby League also has its own set of major competitions, such as the Rugby League World Cup and the State of Origin series in Australia, which is one of the most intense rivalries in the sport. These tournaments attract massive audiences and highlight the unique aspects of Rugby League.
Rugby Sevens: A High-Energy Alternative
How Rugby Sevens Differs from Traditional Rugby
Rugby Sevens is all about speed and skill, with fewer players on the field and shorter match durations. The reduced number of players creates more space on the field, leading to frequent tries and an emphasis on individual brilliance and teamwork.
The Appeal of Rugby Sevens
The high-energy nature of Rugby Sevens, combined with its tournament-friendly format, has made it a popular variation, particularly for international events. Its inclusion in the Olympics has further boosted its global profile, attracting new fans to the sport.
Notable Rugby Sevens Competitions
Key Rugby Sevens tournaments include the World Rugby Sevens Series, which takes place annually and features events in locations like Dubai, Hong Kong, and London. The Sevens format also plays a significant role in the Commonwealth Games and the Summer Olympics.
Touch Rugby and Tag Rugby: Non-Contact Versions
What is Touch Rugby?
Touch Rugby is a variant where players stop advancing the ball when touched by an opponent. This non-contact version focuses on speed, agility, and strategy, making it a popular choice for mixed-gender teams and younger players.
The Basics of Tag Rugby
Tag Rugby is similar to Touch Rugby but involves players wearing a belt with two tags attached. Defenders must remove a tag from the ball carrier to stop play. This version is particularly popular in schools and recreational leagues, as it offers a safe, inclusive way to enjoy the sport.
Benefits of Non-Contact Rugby
Non-contact rugby provides an excellent entry point for those new to the sport or looking to enjoy it in a less physically demanding way. It helps develop key skills such as passing, positioning, and teamwork without the risks associated with full-contact rugby.
The Global Reach of Rugby
Rugby’s Popularity Around the World
Rugby’s global reach is extensive, with the sport thriving in diverse regions, from the traditional powerhouses of the Northern Hemisphere to the rugby-mad nations of the Southern Hemisphere.
Rugby in Europe
Europe is a stronghold for Rugby Union, with countries like England, France, and Ireland boasting some of the world’s best teams and most passionate fans. The Six Nations Championship is a highlight of the European rugby calendar, drawing immense viewership and fierce national pride.
Rugby in the Southern Hemisphere
The Southern Hemisphere is home to some of the most successful rugby nations, including New Zealand, South Africa, and Australia. These countries have produced some of the game’s greatest players and teams, with New Zealand’s All Blacks being particularly iconic for their dominance and distinctive haka.
The Growth of Rugby in North America and Asia
In recent years, rugby has gained traction in North America and Asia, regions traditionally less associated with the sport. The United States has seen a surge in rugby interest, particularly in Rugby Sevens, while Japan’s hosting of the 2019 Rugby World Cup significantly boosted the sport’s profile in Asia.
The Physical and Mental Benefits of Playing Rugby
Physical Fitness and Strength
Rugby is a full-body workout that builds strength, endurance, and agility. The combination of running, tackling, and strategic play ensures that players develop a high level of fitness, making rugby one of the most physically demanding sports.
Mental Toughness and Teamwork
Rugby isn’t just about physicality; it’s a mental game too. Players must remain focused under pressure, make quick decisions, and work cohesively as a team. This mental toughness and emphasis on teamwork translate into valuable life skills both on and off the field.
Social Benefits and Community Spirit
Rugby’s culture of camaraderie and respect, both among teammates and towards opponents, fosters a strong sense of community. Whether at the grassroots or professional level, rugby brings people together, creating lasting friendships and a shared sense of purpose.
The Cultural Impact of Rugby
Rugby’s Influence on National Identity
In many countries, rugby is more than just a sport; it’s a key part of national identity. The All Blacks in New Zealand, the Springboks in South Africa, and England’s rugby team have become symbols of their nations’ resilience, pride, and competitive spirit.
Rugby and Social Change
Rugby has also played a role in social change, particularly in South Africa, where the 1995 Rugby World Cup became a symbol of unity and reconciliation in the post-apartheid era. The sport’s inclusive nature continues to make it a force for positive change worldwide.
Famous Rugby Moments in History
The 2003 Rugby World Cup final, where England clinched victory with a drop goal in extra time, and Japan’s stunning win over South Africa in 2015 are just two examples of how rugby has produced some of sport’s most memorable events.
Rugby’s Major International Competitions
The Rugby World Cup
The Rugby World Cup is the sport’s most prestigious tournament, held every four years and contested by the best teams from around the globe. Winning the World Cup is the ultimate achievement in rugby, with past champions like New Zealand, South Africa, and England etching their names into the sport’s history.
The Six Nations Championship
The Six Nations Championship is an annual competition involving England, France, Ireland, Italy, Scotland, and Wales. This historic tournament is a highlight of the rugby calendar, with intense rivalries and passionate fanbases adding to its allure.
The Rugby Championship
The Rugby Championship is the Southern Hemisphere’s premier rugby competition, featuring Argentina, Australia, New Zealand, and South Africa. Known for its high level of play and fierce competition, this tournament is a showcase of the best rugby the Southern Hemisphere has to offer.
The Future of Rugby
Challenges Facing Modern Rugby
Despite its popularity, rugby faces challenges, including concerns over player safety, the increasing commercialization of the sport, and the need to attract younger audiences.
Innovations and Changes in the Game
Rugby is evolving, with new rules and technologies being introduced to make the game safer and more engaging. Innovations such as the use of video referees and advanced player tracking systems are helping to enhance the spectator experience and improve player welfare.
The Future of Rugby Globally
Rugby’s future looks bright, with the sport continuing to expand into new markets and attract a diverse range of players and fans. The rise of women’s rugby, the growth of Rugby Sevens, and the increasing popularity of the sport in North America and Asia all point to a promising future.
Women in Rugby
The Rise of Women’s Rugby
Women’s rugby has seen tremendous growth in recent years, with more women participating in the sport at all levels. The development of professional leagues and the inclusion of women’s rugby in major tournaments like the Rugby World Cup and the Olympics have further boosted its popularity.
Key Women’s Rugby Competitions
The Women’s Rugby World Cup is the pinnacle of the sport, drawing the best teams from around the world. Other significant competitions include the Women’s Six Nations Championship and the World Rugby Women’s Sevens Series, both of which have helped to elevate the profile of women’s rugby.
Influential Women in Rugby
Many women have made significant contributions to rugby, both on and off the field. Players like New Zealand’s Portia Woodman and England’s Maggie Alphonsi have become icons of the sport, while administrators and coaches continue to break new ground in developing women’s rugby.
Rugby Injuries and Player Safety
Common Injuries in Rugby
Rugby is a contact sport, and with that comes the risk of injury. Common injuries include concussions, sprains, and fractures. However, the sport has made significant strides in recent years to improve player safety through better training, equipment, and medical support.
Advances in Player Safety and Equipment
Modern rugby equipment, including headgear and mouthguards, has improved significantly, reducing the risk of serious injuries. Additionally, stricter enforcement of safety rules and advances in medical care on and off the field have made the game safer for players at all levels.
The Role of Medical Teams in Rugby
Medical teams play a crucial role in rugby, providing immediate care for injured players and ensuring that all safety protocols are followed. The presence of experienced medical professionals at matches and training sessions helps to protect players and manage injuries effectively.
How to Get Involved in Rugby
Joining a Local Rugby Club
Clubs offer opportunities for players of all ages and skill levels, from beginners to experienced players, and provide a supportive environment to learn and enjoy the game.
Rugby for Children and Youth
Rugby is a fantastic sport for children and youth, promoting physical fitness, teamwork, and discipline. Many clubs offer youth programs that teach the fundamentals of rugby in a fun and safe environment, helping to develop the next generation of players.
Conclusion
Rugby is more than just a game; it’s a sport that embodies strength, teamwork, and resilience. Whether you’re playing, watching, or coaching, rugby offers something for everyone. Its rich history, diverse variants, and global appeal make it a unique and enduring part of the world’s sporting landscape. So, whether you’re a seasoned fan or new to the sport, rugby’s spirit of competition and camaraderie is sure to draw you in.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between Rugby and Rugby League?
Rugby Union and Rugby League differ primarily in the number of players, rules regarding tackles, and style of play, with Rugby League being faster and more straightforward.
How long is a typical rugby match?
A standard rugby match lasts 80 minutes, divided into two 40-minute halves, with additional time added for stoppages.
Can rugby be played casually without contact?
Yes, non-contact versions like Touch Rugby and Tag Rugby are popular for casual play, focusing on speed and skill without the physical tackles.
What equipment do you need to start playing rugby?
Basic rugby equipment includes a rugby ball, appropriate clothing (usually shorts and a jersey), boots with studs. And protective gear like a mouthguard and headgear.
How does rugby compare to American football?
While both sports involve carrying the ball to score points. Rugby is continuous with fewer stoppages, has no forward passing, and requires all players to play both offensive and defensive roles.