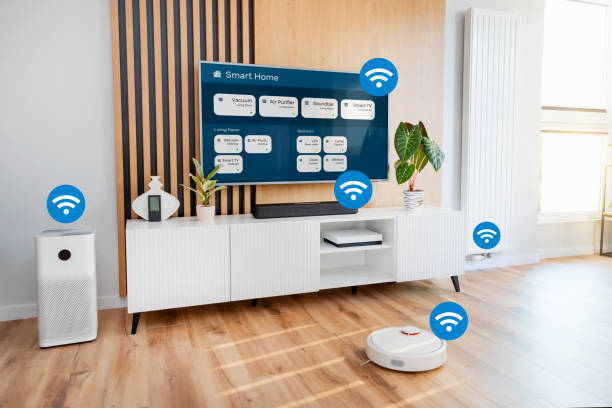
The Internet of Things (IoT) represents a groundbreaking shift in how we interact with technology. By connecting devices and systems through the internet, IoT creates a network of smart devices that communicate and share data. This interconnected ecosystem enhances efficiency, convenience, and innovation across various sectors. This guide delves into the core concepts of IoT, its applications, benefits, challenges, and future trends.
What is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of interconnected devices that communicate with each other over the internet. These devices, often embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies, collect and exchange data to enhance their functionality and provide valuable insights.
Key Components of IoT
- Devices/Sensors: Physical objects equipped with sensors to collect data. Examples include smart thermostats, wearable fitness trackers, and industrial sensors.
- Connectivity: The technology that enables devices to communicate with each other and with central systems. This can include Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular networks, and more.
- Data Processing: The analysis and interpretation of data collected by IoT devices. This is often handled by cloud computing platforms or edge computing systems.
- User Interface: The means by which users interact with IoT devices, such as mobile apps, web dashboards, or voice commands.
How IoT Works
IoT operates through a series of steps that involve data collection, transmission, processing, and action. Here’s a simplified overview of how IoT systems work:
- Data Collection: Sensors on IoT devices gather data from their environment. For instance, a smart thermostat collects temperature readings.
- Data Transmission: The collected data is transmitted over the internet to a central system or cloud platform. This can be done via various communication protocols.
- Data Processing: The central system processes the data, often using algorithms and analytics to derive insights or trigger actions.
- Action/Response: Based on the processed data, the system may perform automated actions, such as adjusting a thermostat setting, sending notifications, or updating a user interface.
Applications of IoT
IoT has diverse applications across various sectors, transforming how we live, work, and interact with technology. Here are some prominent examples:
Smart Thermostats
Smart thermostats, like the Nest Learning Thermostat, adjust heating and cooling settings based on user preferences and patterns. They can be controlled remotely via mobile apps and learn from user behavior to optimize energy use.
Smart Lighting
Smart lighting systems allow users to control lights remotely and set schedules. They can also adjust brightness and color based on ambient conditions or user preferences.
Home Security Systems
IoT-enabled security systems offer features such as real-time video surveillance, motion detection, and remote monitoring. These systems enhance home security by providing instant alerts and easy access to security feeds.
Healthcare
IoT is revolutionizing healthcare by enabling remote monitoring, personalized treatment, and improved patient care.
Wearable Health Devices
Wearable health devices, such as fitness trackers and smartwatches, monitor physical activity, heart rate, and sleep patterns. They provide valuable data for both users and healthcare providers.
Remote Patient Monitoring
IoT-enabled remote monitoring systems allow healthcare professionals to track patient vitals and health metrics from afar. This technology facilitates timely interventions and personalized care.
Smart Medication Management
Smart medication dispensers remind patients to take their medication and can alert caregivers if doses are missed. This ensures adherence to prescribed treatments and improves health outcomes.
Industrial IoT (IIoT)
Industrial IoT involves the application of IoT technologies in manufacturing and industrial processes, enhancing efficiency and productivity.
Predictive Maintenance
IIoT systems use sensors to monitor equipment conditions and predict potential failures before they occur. This proactive approach reduces downtime and maintenance costs.
Asset Tracking
IoT enables real-time tracking of industrial assets, such as machinery and inventory. This visibility improves asset management and operational efficiency.
Process Optimization
IoT data analytics help optimize industrial processes by providing insights into performance, quality, and resource utilization. This leads to increased productivity and reduced waste.
Transportation and Logistics
IoT technology enhances transportation and logistics operations by improving visibility, efficiency, and safety.
Fleet Management
IoT-enabled fleet management systems track vehicle location, fuel consumption, and driver behavior. This data helps optimize routes, reduce operational costs, and enhance safety.
Smart Traffic Management
IoT-based traffic management systems monitor traffic flow, congestion, and environmental conditions. They can adjust traffic signals and provide real-time information to drivers.
Supply Chain Management
IoT improves supply chain management by providing real-time visibility into inventory levels, shipment status, and environmental conditions. This ensures timely delivery and reduces disruptions.
Benefits of IoT
The adoption of IoT offers numerous benefits across different domains. Here are some key advantages:
Increased Efficiency
IoT enhances efficiency by automating processes, optimizing resource use, and providing real-time insights. This leads to cost savings, improved productivity, and streamlined operations.
Enhanced Convenience
IoT technology simplifies daily tasks and improves user convenience. For example, smart home devices allow users to control their environment remotely, while wearable health devices offer personalized insights.
Improved Decision-Making
IoT provides valuable data and analytics that support informed decision-making. Organizations can leverage this information to make strategic decisions, optimize operations, and drive innovation.
Greater Connectivity
IoT fosters greater connectivity between devices, systems, and users. This interconnected ecosystem enables seamless communication and collaboration across various applications and platforms.
Better Quality of Life
IoT improves quality of life by enhancing health management, home automation, and personal convenience. These advancements contribute to a more comfortable and efficient living environment.
Challenges and Considerations
While IoT offers significant benefits, it also presents challenges and considerations that must be addressed:
Security and Privacy
Security and privacy concerns are paramount in IoT. Ensuring that data is protected from unauthorized access and breaches is essential. Implementing robust security measures and encryption is crucial to safeguarding sensitive information.
Data Management
The vast amount of data generated by IoT devices requires effective management and storage solutions. Organizations must ensure that data is processed efficiently and utilized effectively while maintaining compliance with data protection regulations.
Interoperability
Interoperability challenges arise when devices and systems from different manufacturers need to work together seamlessly. Adopting standardized protocols and frameworks can help address these challenges and promote compatibility.
Scalability
Scalability is a key consideration as IoT networks grow and evolve. Ensuring that systems can handle increasing volumes of data and device connections is critical for maintaining performance and reliability.
Ethical and Regulatory Issues
IoT raises ethical and regulatory concerns related to data usage, consent, and transparency. Organizations must navigate these issues and adhere to relevant regulations to ensure responsible and ethical practices.
Future Trends in IoT
The IoT landscape is continually evolving, with several trends shaping its future:
Edge Computing
Edge computing involves processing data closer to the source, rather than relying solely on centralized cloud servers. This reduces latency, enhances real-time processing, and improves overall system efficiency.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration
AI integration with IoT enables advanced data analysis, predictive analytics, and autonomous decision-making. AI algorithms can enhance the functionality and intelligence of IoT devices and applications.
5G Connectivity
5G technology promises to revolutionize IoT by providing faster, more reliable, and higher-capacity connectivity. This will enable more devices to connect and communicate seamlessly, supporting advanced IoT applications.
Enhanced Security Measures
As IoT expands, security measures will continue to evolve. Advanced encryption, multi-factor authentication, and AI-driven threat detection will play a crucial role in protecting IoT systems and data.
Sustainable IoT Solutions
Sustainability is becoming a focus in IoT development. Eco-friendly devices, energy-efficient technologies, and sustainable practices will shape the future of IoT, contributing to a greener and more sustainable world.
Conclusion
The Internet of Things (IoT) represents a transformative shift in technology, connecting devices and systems to create a more interconnected and intelligent world. By understanding IoT’s key components, applications, benefits, and challenges, individuals and organizations can leverage its potential to enhance efficiency, convenience, and innovation.